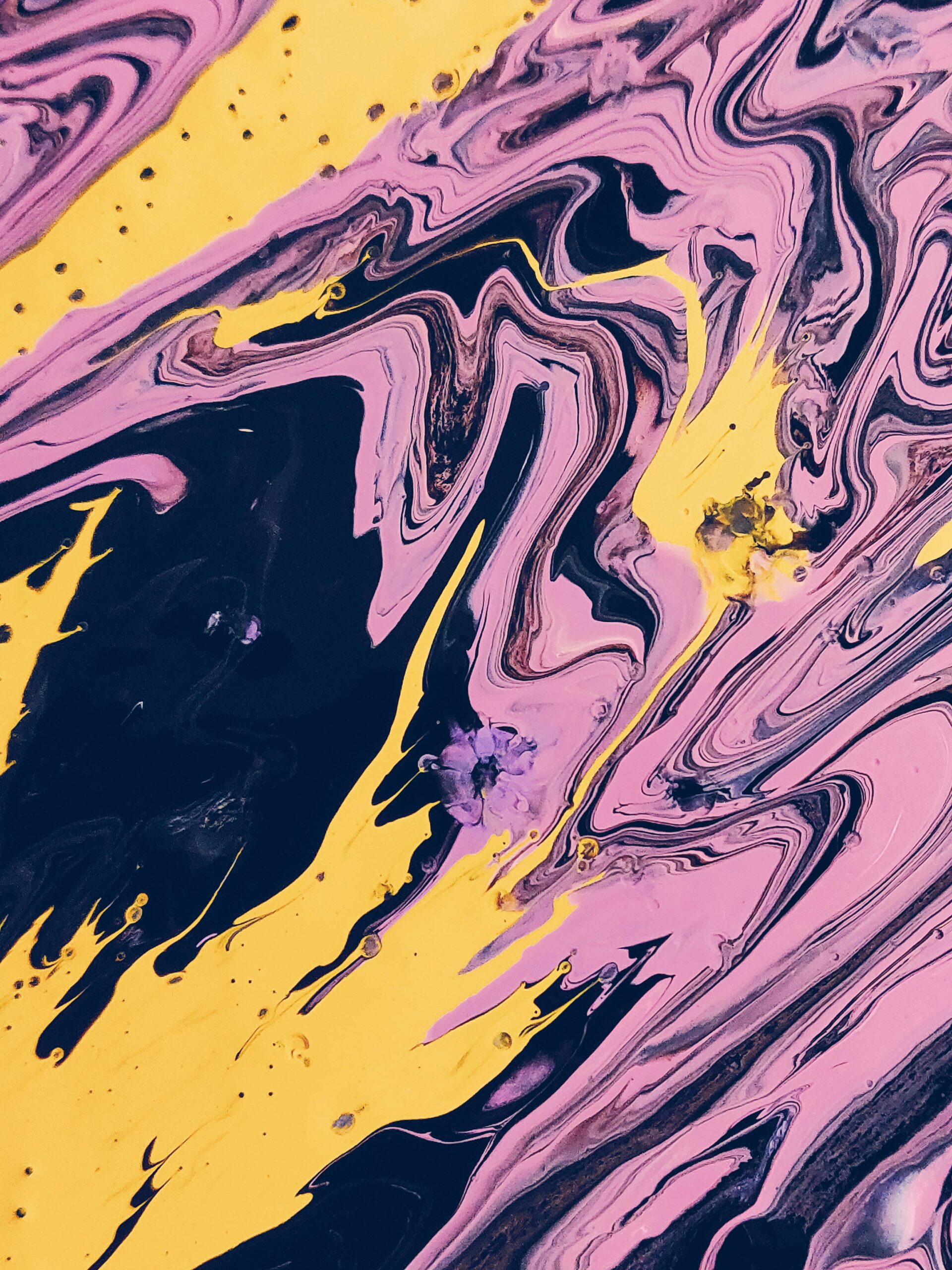
The different styles of Art
1. Realism: Focusing on accurate representation of subjects, often depicting scenes from everyday life.
2. Impressionism: Emphasizing capturing fleeting impressions of light and color, often characterized by visible brushstrokes.

3. Cubism: Presenting subjects from multiple viewpoints simultaneously, with fragmented geometric forms.
4. Abstract Expressionism: Expressing emotions and ideas through spontaneous and non-representational forms.
5. Surrealism: Exploring the realm of dreams and the unconscious, often featuring juxtapositions and unexpected elements.
6. Pop Art: Incorporating popular culture and consumerism, often featuring vibrant colors and mass-produced imagery.

7. Minimalism: Stripping art down to its essential elements, often using simple geometric shapes and monochromatic color schemes.
8. Fauvism: Using bold and vibrant colors, emphasizing expressiveness over realistic representation.
9. Renaissance: Reviving classical ideals with a focus on realistic proportions, perspective, and human anatomy.
10. Baroque: Characterized by grandeur, drama, and elaborate ornamentation, often associated with religious subjects.

11. Art Nouveau: Emphasizing organic and flowing lines, often featuring intricate and decorative motifs.
12. Pointillism: Creating images using small dots or points of pure color, which visually blend when viewed from a distance.
13. Dadaism: Challenging traditional notions of art, often incorporating found objects and nonsensical elements.
14. Expressionism: Conveying subjective emotions and inner turmoil through distorted and exaggerated forms.

15. Symbolism: Using symbolic imagery to express metaphorical or mystical ideas.
16. Post-Impressionism: Building upon Impressionism, featuring more structure and expressive brushwork.
17. Op Art: Optical illusions and visual effects, often employing geometric patterns and contrasting colors.
18. Constructivism: Focusing on the combination of art and industrial materials, often emphasizing functionality and social engagement.

19. Art Deco: Incorporating geometric forms, sleek lines, and luxurious materials, often associated with the 1920s and 1930s.
20. Street Art: Artistic expressions displayed in public spaces, encompassing various styles such as graffiti, murals, and stencil art.
These are just a few examples, and there are many more art styles and movements that have shaped the history of art.